Hoverboards, a term now synonymous with innovative and personal transportation, have rapidly gained popularity in the tech sphere and among thrill-seekers globally. Despite their name suggesting a futuristic mode of travel that defies gravity, hoverboards, in reality, are grounded in the present and operate on solid ground. But what precisely is a hoverboard, and when was it invented? This blog post aims to answer these questions and more.
Table of Contents
What Is a Hoverboard?
A hoverboard, also known as a self-balancing scooter, is a personal transport device. It’s a gadget that, despite its name, doesn’t actually hover off the ground. Instead, it rolls on the ground on two wheels, powered by rechargeable batteries. The term ‘hoverboard’ found its popularity in the Back to the Future movie series, which showcased a similar-looking device that floated above the ground.
In reality, hoverboards are two-wheeled devices that use sensors to keep balance and are controlled by the feet. They have a platform for the rider to stand on, with a wheel on either side, and use electric power to run. The rider controls the speed and direction by shifting their weight. Modern hoverboards are controlled by the rider’s balance, hence the alternative name – self-balancing scooters.

Do Hoverboards Really Hover?
The name ‘hoverboard’ is admittedly a bit misleading. Modern hoverboards don’t truly hover – they roll on wheels. The term ‘hover’ in the name is more of a nod to the futuristic technology and the sense of ‘floating’ you might feel while gliding on one.
However, the concept of a real, hovering board isn’t just a pipe dream. In recent years, several companies and inventors have experimented with hover technology. For instance, the Hendo Hoverboard and the Lexus Slide are two examples that use magnetic levitation to achieve hover-like movement. However, these hoverboards are still in the prototype stage, are prohibitively expensive, and require specific surfaces to operate, making them far from practical for everyday use.
When Did Hoverboards Come Out?
The hoverboards that we know today were first introduced to the consumer market in 2013. But the concept of hoverboards has been present in our collective imagination for much longer.
The idea of a personal, levitating transport device captured the public’s imagination in the 1980s, thanks to popular culture references like the Back to the Future film series. The first commercially successful hoverboards were launched by Chinese companies and quickly gained popularity worldwide, thanks to their novelty and the growing interest in personal electric transportation devices.
Who Invented The Hoverboard?
The hoverboard was the brainchild of Shane Chen, a Chinese-American inventor. Chen is a prolific inventor with numerous patents to his name, but he is best known for the hoverboard. He patented the device in 2013 under his company, Inventist, and introduced it at the Consumer Electronics Show in Las Vegas in 2014.
Unfortunately, Chen’s design was quickly copied by other manufacturers. Despite having a patent, he found it difficult to enforce his rights, and the market was soon flooded with cheap knock-offs. This led to a lot of confusion about the origin of the hoverboard and who its true inventor was.
Key Milestones in Hoverboard Development
The journey of hoverboards from concept to reality has seen numerous major milestones over the years. Let’s take a walk down memory lane:
- 2013: Shane Chen patents the Hovertrax, introducing the world to the concept of a self-balancing personal transport device.
- 2014: Several companies take notice of Chen’s invention and start producing their own versions of hoverboards. This year marks the beginning of the hoverboard boom, with these nifty devices quickly becoming a common sight in many urban areas.
- 2015-2016: Safety concerns arise due to reports of hoverboards catching fire, largely due to issues with their lithium-ion batteries. This leads to a temporary halt in hoverboard sales and stricter regulations being implemented. Hoverboard manufacturers are forced to improve the safety features in their models, leading to the introduction of hoverboards with fire-resistant casings and better-quality batteries.
- 2017-present: Advances in battery technology and better balancing mechanisms lead to safer, more efficient hoverboards. Modern hoverboards often feature UL certification, ensuring they meet stringent safety standards. The present-day hoverboard market is characterized by a wide variety of models catering to different user needs, from off-road hoverboards for adventurous riders to compact models for urban commuters.
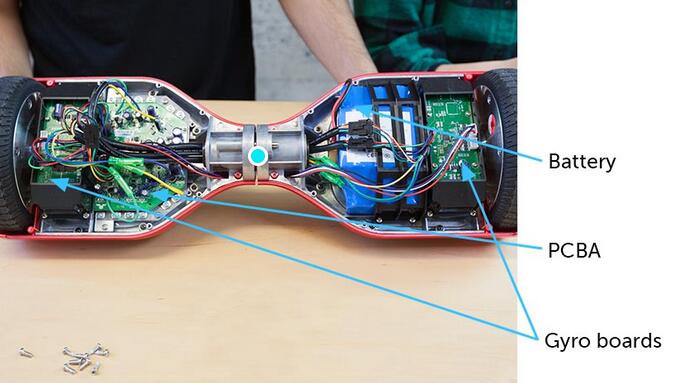
What Are Hoverboards Made Of?
If you’re wondering what hoverboards consist of, look closely at the following section. Let’s quickly dissect hoverboards and learn about the main parts and their primary function.
Gyroscope
The gyroscope is the most critical component of a hoverboard. It’s the part that adjusts the platform’s tilt to keep you balanced, which is why some people call hoverboards “gyro scooters.”
Microprocessor
Another essential component of a hoverboard is the microprocessor. This part regulates the amount of power going to the two motorized wheels.
Battery
Hoverboards run on rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. They keep the hoverboard’s electrical power as well as charge. About 4 hours of charging provides up to 8 miles of riding. However, this mainly depends on your hoverboard model and other factors such as weight, speed, etc.
Motor
The motor plays a vital role in the operation of a hoverboard. This component gets information from the logic board and powers the two motorized wheels when tilted.
IR sensors
Infrared sensors, often called IR sensors, measure the presence of objects and distance. They’re utilized for many different functions in operating a self-balancing scooter.
Tilt and speed sensors
The tilt and speed sensors control the device’s speed by measuring how fast the two wheels turn and communicate with the logic board and gyroscope, so they’re essential.
Logic board
The logic board processes the information from different sensors and forwards the data to the motors, which provides the needed movements and directions. It also ensures the balance of the device.
Pressure pads
The pressure pads inform the logic board when someone’s riding and in which direction they want to move. When you desire to ride a hoverboard, you should place your feet on the pressure pads.
Two wheels
The wheels of hoverboards vary in size. Therefore, the size of the wheels depends on the manufacturer. If you’re looking for a more advanced, off-road hoverboard, opt for a model with 8-inch wheels.
Power switch
Hoverboards have a power switch that turns the board on and off. Most models have a charging port as well. However, you can purchase this part online separately, too! Other extra features include speakers, LCD screens, LED lights, etc.
How Do Hoverboards Work?
The technology behind hoverboards is fascinating. The concept is simple: the hoverboard responds to the rider’s shift in weight and adjusts its speed and direction accordingly. However, the mechanics and electronics that make this possible are complex.
The key to a hoverboard’s operation is its sensors. The gyroscope and acceleration sensors detect the user’s body movement. When the rider leans forward, the hoverboard increases power to the front wheel, causing the board to move forward. Similarly, leaning back decreases power, slowing the board or making it move backward. The rider controls turning by applying pressure with one foot.
Are Hoverboards Legal?
Hoverboards aren’t legal everywhere. The only countries with official hoverboard laws include New York and California. For instance, they’re banned from public spaces in New York City.
The New York State Traffic Law 114-d says that public officials consider these electric devices personal but illegal assistance devices. They’re semi-legal in California because Assembly Bill No. 604 limits speed, age, and permitted spaces for use. Children under the age of 16 can’t utilize hoverboards in public.
Furthermore, if you’re over 16 and riding a hoverboard in a permitted space, you can’t surpass 15 mph. In CA, you will also need a helmet if riding a hoverboard, and you should only ride it on streets with speed limits under 35 mph. As you can notice, the laws differ from place to place worldwide.
Germany, England, Wales, The Netherlands, Scotland, Mecca, Hong Kong, Australia, and Toronto also have some regulations on using these devices! So, inform yourself before you take a ride.

Are Hoverboards Safe?
Thankfully, hoverboards aren’t dangerous as they were back in 2015. Now, they’re 100% safe because UL-certified lithium-ion batteries power them.
Almost all electric devices, including hoverboards, use this type of battery because they’re small but can keep a lot of electricity. However, they can also overheat and explode.
Therefore, you should always purchase from a retailer you already know and trust. According to the US Consumer Product Safety Commission, you should avoid buying hoverboards at random websites or suspicious mall kiosks that don’t seem to know much about these units.
If you don’t think you could locate the seller again in case a problem surfaces with your hoverboard, that should be your red flag not to do business with that person or company.
Furthermore, check for certification labels such as ETL or UL emblem on the package, item, and user manual. The things confirm that your hoverboard was carefully inspected at a lab for safety and passed all tests. However, stay vigilant even if you notice the labels on your device.
Manufacturers who don’t care about these customers’ safety will slap a fake emblem on their products. UL works closely with Interpol and US Customs to prevent this problem.
Giants like Target and Amazon sell hoverboards with certifications for chargers and batteries. However, that doesn’t mean the whole hoverboard has been certified, so stay cautious. Some companies even report utilizing Samsung batteries, but they’re faked.
Overall, when used properly, hoverboards don’t pose a risk to riders. Don’t forget about safety gear if you want to buy a self-balancing scooter. Always wear a helmet, elbow pads, knee pads, and wrist guards, especially if you’re a beginner. Also, make sure it’s a UL-certified model.
Lastly, if you’re purchasing a hoverboard for your kids, note that some hoverboards come with minimum recommended ages (5-7 years old) and weights (45-50 pounds).
Modern Day Hoverboards
Today’s hoverboards are a far cry from their early counterparts. They’re not just basic self-balancing scooters anymore – they’re sophisticated devices loaded with a host of features designed to enhance user experience.
Many hoverboards now come with LED lights for visibility, Bluetoothspeakers for entertainment, and smartphone compatibility for easy control and customization. They also have robust safety features, such as fender bumpers, non-slip foot pads, and learning modes for beginners.
Moveover, the design and aesthetics of hoverboards have also evolved. They now come in a variety of colors and patterns, with some even offering customizable LED lights. This allows riders to express their unique personality and style while zipping around on their hoverboards.
What’s Next for Hoverboards?
Looking ahead, the future of hoverboards seems incredibly promising. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more improvements and innovations in hoverboard design and functionality.
One of the key areas of focus is the battery. With advances in battery technology, future hoverboards could have longer runtimes and shorter charging times. This would make them even more convenient for commuting and long rides.
Another area ripe for innovation is the riding experience. Companies are continuously working on improving the balancing mechanism and ride smoothness of hoverboards. We can expect future models to offer even more stable and comfortable rides.
Moreover, some companies are even experimenting with “true” hoverboards that can levitate above the ground! While still in the early stages of development, this could revolutionize personal transportation and bring us one step closer to the hoverboards we’ve seen in science fiction.










